Marking Gauge [kebiki]
Kebiki
Kebiki

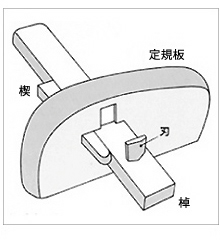
Marking Gauge is a tool that draws lines on the surface of flat wood. It is a tool equipped with a Marking Gauge blade, which draws a thin pole on a board that becomes Ruler and borders on the end of this pole. By sliding the Ruler board along the side of the board, the Marking Gauge blade at the tip of the rod will mark the surface. Since the line is thinner than the ink line, it is used for precision finishing. Marking Gauge can be broadly divided into "Suji Marking Gauge" which signifies the line, and "Wari Marking Gauge" which breaks the thin plate directly with a Marking Gauge blade. "Wari Marking Gauge" is a slightly larger Marking Gauge.
Muscle Marking Gauge is used to draw lines parallel to the standard surface. Depending on the type and purpose of work, there are also two-saosuji Marking Gauge and Nagasao Marking Gauge. Two rodsuji Marking Gauge can use two rods on both sides of a single Ruler plate. Two types of lines can be ruled in one Marking Gauge, such as the blade of one pole, the blade of the instep is attached to the instep, the Ruler plate is turned over and the other blade is the blade of Otsu. Nagasao Marking Gauge is a long pole designed to rule a line on a wide slope.

From left, split Marking Gauge, Musuji Marking Gauge, Nisuji Marking Gauge, Chosao Marking Gauge
The Marking Gauge is slightly larger and sturdy than Muscle Marking Gauge, and is used when grinding thin sheet material.
Kama Marking Gauge has two L-shaped Marking Gauge blades, unlike Musuji Marking Gauge and Wari Marking Gauge. Slide the long part of the L-shaped part on the pole to adjust the width and fasten it with a screw. At Musuji Marking Gauge, the pole at the tip of the Marking Gauge blade is disturbed.
The Marking Gauge is a cross-sectional square camphor with a ruled claw instead of a Marking Gauge blade. There are several types of poles, such as two or four. It can be used to determine the width of a handle hole or groove, and can draw several lines at the same time. It is often used in the work of fittings and fingers.
The white paper is used to draw accurate lines on components using kushaku or makigane. It is often used in work such as fittings and finger objects. There are also two white papers that draw two parallel lines.

From the left to the left, Kama Marking Gauge, Chisel Marking Gauge (four pieces), Chisel Marking Gauge (one piece) front to the left, Kama Marking Gauge single blade, white paper, Nicho white paper
Basic information
Special Exhibition
Permanent exhibition