Plane [kanna]
Kanna
Kanna

Oh shakurikan
It is used to cut the bottom of a long groove with a wide width, such as a kamoi or a sill. The width of the upper end of the table is wider and sturdy than the ordinary bottom plane, but it is easy to grip by removing the steps. The blade width is generally 5 minutes, 6 minutes, and 7 minutes.
I'm going to be there.
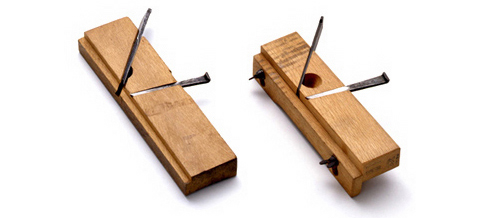
Used to finish the bottom of a groove such as a moi or a silling. The blade width ranges from 3 minutes to 1 inch, but most of them are 5 to 7 minutes. Depending on the shape of the blade or table, it is classified into western, eastern, comb, and Osaka type (Fig. 1). The blade of the plane is generally shaped like a chisel blade. This blade is made into a rectangular table with a cross section, a west-shaped table with one side or both sides of the lower end are called an east-shaped type, and a bow-shaped table with a gentle curve like a comb shape. The Osaka type refers to a normal plane blade similar to a flat plane, with a narrow width blade and a stand on both sides of the lower end. The Osaka-type table has a hole on the table so that plane scraps come out from above, but the other bottom-line planes have a structure where plane scraps come out from the side of the table. (Refer to the photo) In the east and Osaka types, the lack of steps in the table becomes Ruler and the depth of the groove is determined. The comb type is mainly used for small work. Some blades of the decisive plane have diagonal blades so that plane scraps can easily be spiralized (streak blade).
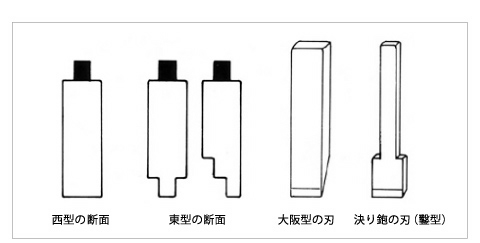
Figure 1 Bottom Plane

From left, rough plane, bottom plane (comb type), bottom plane (west type), bottom plane (Osaka)
I'm gonna be
For rough decision of the bottom of the groove, such as kamoi and silling. It has a shape with Ruler on the side of the Osaka-style bottom. By adjusting the Ruler, the position of digging the groove is determined. The blade width is generally 5 minutes, 6 minutes, and 7 minutes.
Use thin groove for Shaving. A stand with the required groove width path (the lower end part that protrudes as much as the width of the plane blade to cut the groove part) has a Ruler that can adjust the distance with screws, and the structure looks somewhat mechanical. Adjusting the Ruler determines the position of the groove. The blade width is generally between 5 rin to 5 minutes. Until a mechanical one was formed, it was called a small hole punch.
I'm afraid I'm going to do it.
It has almost the same structure as the mechanical plane, but there is no part of the road, and the tip of the wedge inserted from the top of the table comes out like a dabo near the blade edge to replace it. Since there is no road behind the plane blade, small holes that have been stuck (finished halfway) can be shaved (Fig. 2). The blade width is generally 1 to 3 minutes.
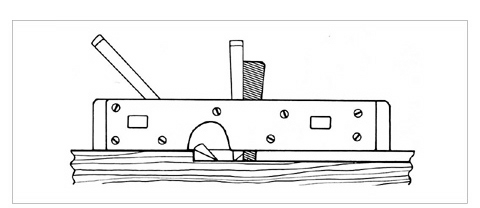
From left, base city plane, machine decision plane, small hole punch (back), Dabo decision plane (back)
The lower end of the table is missing for the blade width. The lack of this stage is made into Ruler. (Fig. 3). Some are equipped with Ruler, which is adjusted with screws, similar to machine planes. The blade width is determined by adjusting the Ruler, and the depth of the phase gap is determined.
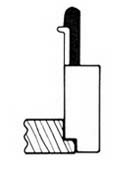
Figure 3 Phase Plane
From left side, phase plane, phase plane (with ruler)
Use an ant-shaped part for Shaving. The lower end of the table is cut off diagonally according to the blade width, the convex part is cut (for male trees), and the convex part is Shaving part (for female trees) with the bottom part being determined and the other lower end is diagonally cut (for male trees). For male trees, a screw-type Ruler is attached, and some can adjust the blade width or the depth of the ant pattern. A couple ant decision plane for male and female trees has also been devised.
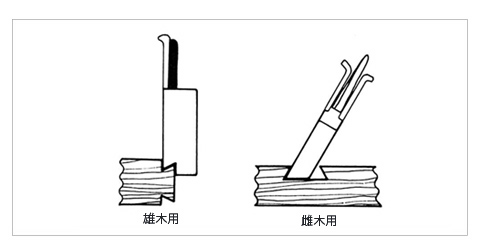
Figure 4 Ants are bored

From the left, ant decision plane, ant decision plane (with ruler)
I'm sucky.
It is used to make Kumite of shoji door or Fusuma. A large number of kumikos can be correctly aligned, tightened with a scrap metal, and the necessary parts can be shaved off sideways at the same time (Fig. 5). The blade width is generally 1 to 3 minutes.
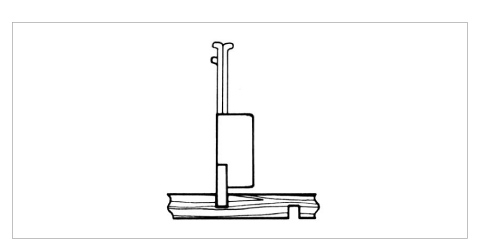
Figure 5 Kumite-determined plane
The structure is very similar to the Osaka-type bottom plane, but the width is wide and the lack of steps is deep. It is used to cut the sliding groove of the door in the window frame of the upper and lower windows used for Western-style architecture.

From the left, Kumite-determined plane, window frame fixed plane (back)
Basic information
Special Exhibition
Permanent exhibition